In modern water treatment systems—whether for municipal wastewater plants or industrial sewage treatment—the gear reducer plays a crucial role in ensuring stable performance, low energy consumption, and reliable long-term operation. For manufacturers of water treatment equipment, the choice of gear reducer directly impacts equipment quality, operating costs, and customer satisfaction.
This article offers a comprehensive guide to selecting the most suitable gear reducers for different types of water treatment applications. It also explores cost-control strategies, supplier evaluation methods, and common procurement pitfalls, empowering factories to make smarter, data-driven purchasing decisions.
![1 1]()
1. Importance of Gear Reducers in Water Treatment Equipment
A gear reducer reduces motor speed while increasing torque, ensuring that equipment like screen scrubbers, aeration blowers, and sludge dewatering machines operates efficiently and reliably. The right reducer enhances energy efficiency, minimizes maintenance frequency, and extends the service life of the equipment.
Poor reducer selection, on the other hand, leads to higher electricity bills, frequent breakdowns, and dissatisfied customers. For this reason, water treatment equipment manufacturers must align reducer specifications with real-world application conditions.
![2 2]()
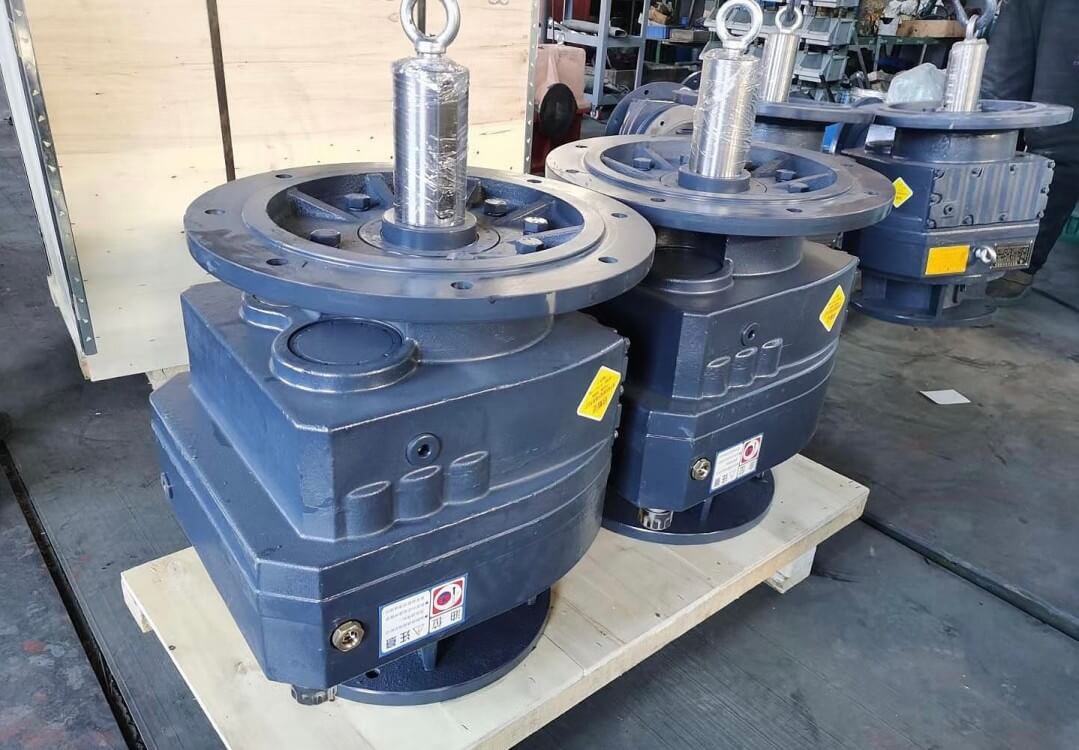
2. Matching Gear Reducers with Different Water Treatment Equipment
Every water treatment system presents unique operating conditions and load profiles. A "one-size-fits-all" approach doesn’t work in this field. The correct strategy is to match reducer design, material, and torque output to the equipment type.
2.1 Screen Scrubbers: Prioritize Durability and Easy Maintenance
Operational Challenge:
Screen scrubbers often encounter impact loads from debris and large particles clogging the screens. Such conditions can quickly wear out standard reducers.
Optimal Solution:
Use hardened cylindrical gear reducers with a tooth surface hardness of HRC58 or higher, capable of withstanding short-term overloads up to 1.5× rated torque. This ensures stability even under heavy shocks.
Recommended Features:
Modular, split-housing design for easy maintenance
Corrosion-resistant coatings for long-term operation in humid environments
Oil-immersed lubrication to minimize friction and wear
Case Example:
A Jiangsu-based water treatment manufacturer adopted this configuration and reported a 40% reduction in failure rates in their screen scrubbers. As a result, customer satisfaction and after-sales reliability improved significantly.
2.2 Aeration Fans: Focus on Precision and Energy Efficiency
Operational Challenge:
Aeration fans are among the highest energy consumers in a wastewater treatment facility. The efficiency of their reducers directly affects overall operational costs.
Optimal Solution:
Select planetary gear reducers with transmission efficiencies above 96%, offering fine speed control as low as 0.1 r/min. When paired with a variable frequency drive (VFD) motor, they allow precise control over airflow and oxygen delivery, ensuring optimal energy use.
Recommended Features:
Forced air-cooling design to prevent overheating
Low-backlash gearing for stable speed regulation
Noise-reduction housing for quieter operation
Case Example:
A Guangdong-based manufacturer equipped its aeration fans with high-efficiency planetary reducers. The upgrade reduced energy consumption by 12%, resulting in lower electricity costs and a stronger competitive edge during project bidding.
2.3 Sludge Dewatering Machines: Prioritize High Torque and Longevity
Operational Challenge:
Sludge dewatering equipment runs continuously under high torque loads. Poor-quality reducers in these systems lead to overheating and rapid component degradation.
Optimal Solution:
Use two-stage, hardened-tooth reducers with a reduction ratio of at least 1:100, allowing motor speed reduction to 5–10 r/min. This ensures consistent torque delivery for heavy-duty operations.
Recommended Features:
Oil bath lubrication for efficient cooling
Extended oil change cycle of 8,000+ hours
Reinforced bearings for continuous load capacity
Result:
This configuration extends service life, minimizes unplanned downtime, and reduces maintenance frequency, improving operational stability in sludge management.
![3 3]()
3. Key Procurement Priorities for Manufacturers
Factory procurement teams must balance price, quality, and after-sales support. Understanding the total cost of ownership and setting strict supplier criteria ensures long-term profitability and reliability.
3.1 Cost Control: Focus on Lifecycle Value, Not Unit Price
Many factories mistakenly prioritize low upfront prices, only to face higher maintenance costs later. The real focus should be on total lifecycle cost, including purchase, operation, and service expenses.
Example:
For a grate decontamination machine, a hardened-tooth reducer may cost 15–20% more initially than a soft-tooth model. However, its service life is three times longer, and maintenance costs are 50% lower.
Recommendation:
Develop a cost evaluation model that includes:
This approach ensures cost-effectiveness over the entire operational cycle.
3.2 Quality Control: Define Measurable Acceptance Standards
To prevent suppliers from substituting inferior components, buyers should establish strict quality benchmarks before procurement.
Key Indicators:
Additional Recommendation:
Request a 1,000-hour no-load test report demonstrating acceptable noise, vibration, and thermal stability before accepting large orders.
3.3 After-Sales Support: Ensure Reliability and Fast Response
After-sales service can be a major differentiator among suppliers. Manufacturers should:
Require a minimum 18-month warranty, covering core components like gears and bearings.
Define response times for technical issues—ideally within 24 hours.
Verify that suppliers offer local service teams or remote diagnostic support.
A strong after-sales partnership reduces downtime and boosts customer confidence.
![4 4]()
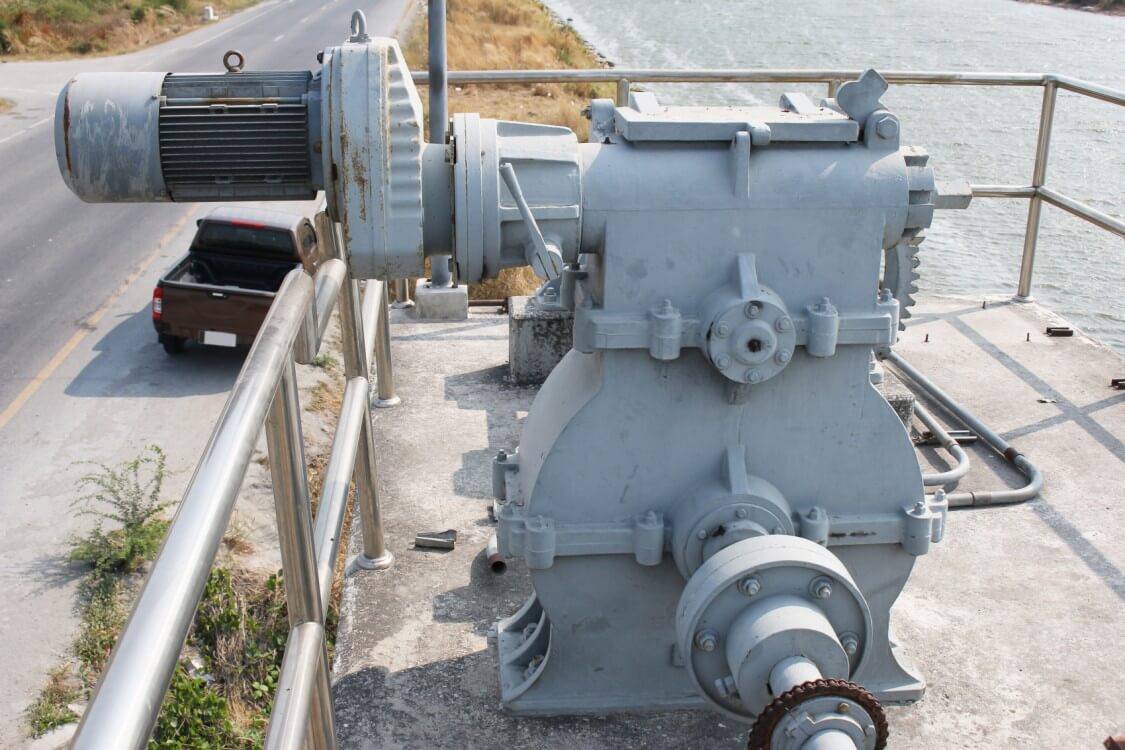
4. Procurement Risks and Mitigation Strategies
Understanding common procurement pitfalls helps avoid costly mistakes.
4.1 Common Mistake 1: Prioritizing Price Over Performance
Some factories opt for the cheapest reducers to save on initial costs. However, low-quality reducers often lead to early failures, gear wear, or bearing breakdowns, resulting in expensive warranty claims.
Solution:
Establish a cost-quality balance model. Evaluate suppliers not just on pricing but also on:
4.2 Common Mistake 2: Ignoring Real-World Operating Conditions
Selecting reducers without considering the working environment—such as humidity, temperature, and corrosion levels—can cause premature failures.
Solution:
Create a “Reducer Selection and Operating Condition Survey Form.”
Before finalizing a purchase, have sales engineers collect site-specific data, including:
Ambient temperature and humidity
Exposure to chemicals or corrosive gases
Operating cycles and load variations
This ensures the chosen reducer matches the actual application conditions.
![6 6]()
5. Real-World Case Study: Lessons from Successful Procurement
A municipal wastewater project in eastern China initially used low-priced soft-tooth reducers in its screen scrubbers to save on costs. Within six months, gear breakage occurred, leading to significant after-sales repairs and customer complaints.
In the next procurement cycle, the factory switched to hardened cylindrical gear reducers. Although the purchase cost increased by 18%, the new models ran three years without failure, and after-sales costs dropped by 60%.
More importantly, the improved reliability helped the company win additional municipal contracts, strengthening its market position.
![7 7]()
6. Strategic Approach for Future-Ready Water Treatment Manufacturers
In today’s evolving water treatment industry, gear reducers are not just functional components—they’re a strategic investment. The right choice boosts product competitiveness, reduces total operating costs, and enhances customer trust.
Key Takeaways:
Match reducer design precisely to each type of equipment.
Balance short-term cost with long-term performance.
Enforce measurable quality standards and testing protocols.
Choose suppliers with responsive after-sales service.
![8 8]()
7. Embracing the Future: Intelligent Gear Reducers
The future of gear reducers in water treatment lies in digital transformation. Modern intelligent reducers integrate sensors and IoT systems that monitor parameters such as:
These smart systems enable predictive maintenance, reducing unplanned downtime and providing valuable operational data for end users.
Factories partnering with digital-ready suppliers can offer advanced, data-driven solutions that deliver added value and help them expand market share in a highly competitive landscape.
![9 9]()
8. Conclusion
The application of gear reducers in water treatment equipment is vital for achieving energy-efficient, reliable, and cost-effective operations. By aligning reducer specifications with actual performance requirements, manufacturers can significantly enhance both product quality and operational stability.
Factories that take a strategic approach—focusing on lifecycle cost, quality assurance, and intelligent supplier partnerships—can achieve the ultimate goals of:
As the water treatment industry moves toward automation and digitalization, gear reducers will continue to evolve, serving not just as power transmission units but as intelligent performance enhancers in the next generation of environmental technology.
English
العربية
Français
Русский
Español
Português
Deutsch
italiano
日本語
한국어
Nederlands
Tiếng Việt
ไทย
Polski
Türkçe
Bahasa Melayu
Filipino
Bahasa Indonesia
magyar
Română
Čeština
Монгол
қазақ
Српски
हिन्दी
فارسی
Slovenčina
Slovenščina
Norsk
Svenska
українська
Ελληνικά
Suomi
Հայերեն
Latine
Dansk
Hrvatski
Gaeilge
Eesti keel
Oʻzbekcha
latviešu
Беларуская мова
Български
ქართული
guarani
ʻŌlelo Hawaiʻi
Lietuvių
Lëtzebuergesch
Македонски
Malti
मराठी