Introduction
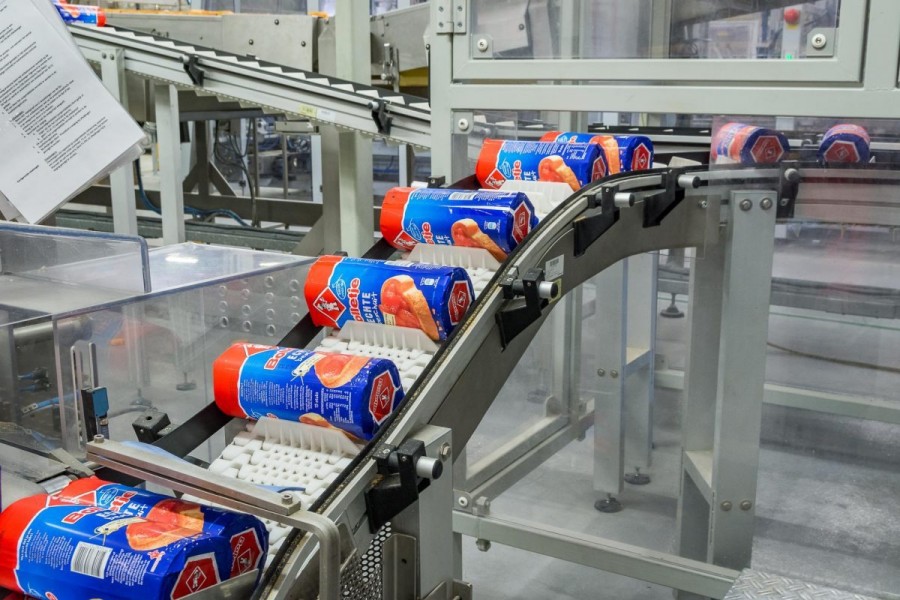
Ever stopped to think about how your groceries glide smoothly along the checkout counter or how packages zip through a warehouse? That’s the magic of conveyor systems, and at the heart of every one of them is an electric motor. These unsung heroes keep industries moving—literally. From manufacturing plants to airports, electric motors power the belts, rollers, and chains that make modern logistics possible.
But why are they so critical, and what makes them tick? In this article, we’ll dive into the world of electric motors in conveyor systems, exploring their benefits, challenges, and how to keep them running like a dream. Ready to roll? Let’s get started!
![Introduction Introduction]()
What Are Conveyor Systems?
Picture a conveyor system as the backbone of material handling. It’s a setup of belts, rollers, or chains designed to move goods from point A to point B with minimal effort. Whether it’s hauling heavy crates in a warehouse or shuttling luggage at an airport, conveyors make life easier. They’re the silent workhorses behind industries like manufacturing, mining, food processing, and logistics. Without them, we’d be stuck lugging stuff around by hand—yikes!
Component of Conveyor Systems
| Component | Description | Role |
| Conveyor Medium | Conveyor belt or rollers | Transports goods |
| Drive System | Electric motor and transmission system | Provides power to move the conveyor medium |
| Support Structure | Frames and supports | Holds the system in place |
Types of Conveyor Systems
1. Belt Conveyor Systems
Overview:
The most widely used type, belt conveyors consist of a continuous loop of material (belt) that rotates over pulleys, with their continuous loops, are perfect for moving lightweight items like packages or food.
Ideal For:
Common Applications:
Advantages:
![Belt Conveyor Systems Belt Conveyor Systems]()
2. Roller Conveyor Systems
Overview:
Roller conveyors use cylindrical rollers placed in a frame to move items, either manually or by gravity/motors.
Types:
Ideal For:
Applications:
· Warehouses
· Packaging lines
· Shipping areas
Advantages:
![Roller Conveyor Systems Roller Conveyor Systems]()
3. Chain Conveyor Systems
Overview:
Chain conveyors use linked chains to transport heavy items along a fixed path.
Ideal For:
Applications:
Advantages:
![Chain Conveyor Systems Chain Conveyor Systems]()
Conveyor systems are essential components in various industries, used to transport materials from one location to another with minimal human effort. These systems increase efficiency, enhance safety, and streamline processes in manufacturing, packaging, mining, food processing, airports, warehouses, and more. Not all conveyors are created equal. Each type has its own vibe, but they all rely on one thing to keep moving: electric motors.
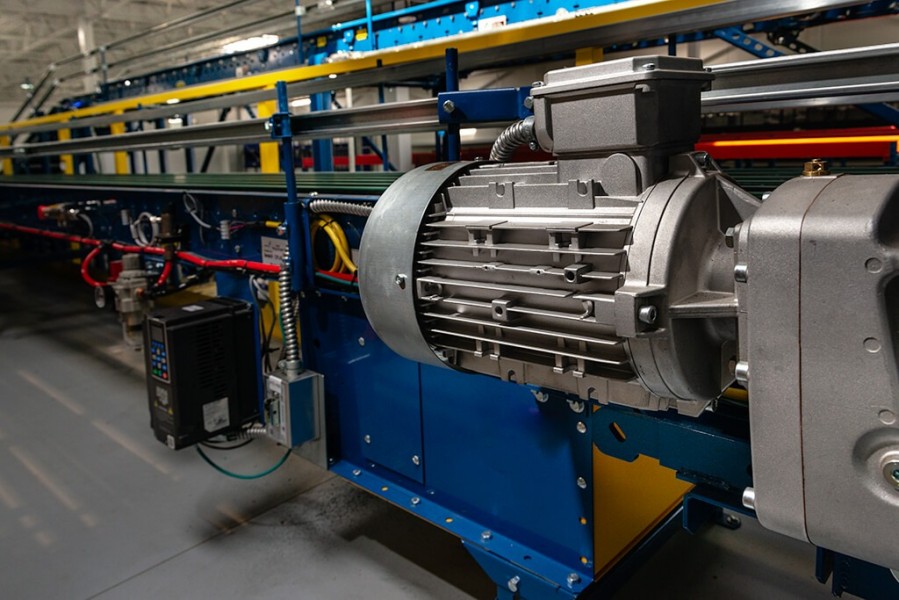
The Heart of Conveyor Systems: Electric Motors
If a conveyor system is the body, the electric motor is the beating heart. Without it, the whole operation grinds to a halt. Electric motors convert electrical energy into mechanical motion, driving the belts or rollers that keep goods flowing. They’re like the engine in your car—without them, you’re not going anywhere. Their reliability and power make them indispensable in keeping conveyor systems humming along.
How Electric Motors Power Conveyors
So, how do these motors work their magic? It’s all about rotation. An electric motor generates a spinning motion through electromagnetic fields, which turns a shaft connected to the conveyor’s drive system. This could mean spinning a pulley on a belt conveyor or driving a gear on a chain system. It’s like pedaling a bike—the motor’s “pedaling” keeps the conveyor moving smoothly. The beauty? Motors can be fine-tuned for speed and power, making them perfect for any conveyor setup.
1. Driving Motion: The Core Function of the Motor
At the most basic level, electric motors convert electrical energy into mechanical motion, which powers the movement of conveyor belts, rollers, or chains. Without this motorized drive, the conveyor would be static and useless.
How it works:
· The motor shaft rotates, typically through a gearbox, which then turns pulleys or rollers.
· This motion propels the belt or components, moving products from one point to another.
Key Impact:
2. Ensuring Precise Speed and Load Control
Electric motors enable precise control over conveyor speed, which is essential for tasks like product sorting, assembly, or packaging.
How Motors Enhance Control:
Benefits:
· Prevents spillage or product damage.
· Matches conveyor speed to upstream/downstream processes.
· Reduces wear and tear from sudden starts or stops.
![The Core Function of the Motor The Core Function of the Motor]()
3. Energy Efficiency and Cost Reduction
Electric motors—especially those with IE3 or IE4 efficiency ratings—are built to deliver high performance with minimal energy consumption.
Why Efficiency Matters:
· Motors are often running 24/7 in industrial facilities.
· Energy-efficient motors reduce power usage, lowering utility bills.
· Less heat generation means longer motor life.
Best Practices:
· Use motors with high-efficiency ratings.
· Integrate with VFDs to match speed with actual load demands.
· Perform regular motor maintenance to ensure optimal performance.
4. Enhancing Conveyor System Safety
Motors in conveyor systems also play a vital role in safety, particularly when integrated with brake motors or emergency stop systems.
Safety Features Supported by Motors:
· Electromagnetic brakes for immediate stopping.
· Overload protection via thermal relays.
· Reverse motion prevention in inclined conveyors.
These features are crucial in applications involving people, heavy loads, or high-speed operations.
![Enhancing Conveyor System Safety Enhancing Conveyor System Safety]()
5. Enabling Automation and Smart Control
Modern electric motors support digital communication and programmable logic controller (PLC) integration, making them perfect for smart factories.
Smart Features:
· Real-time feedback on load, speed, temperature.
· Remote diagnostics and troubleshooting.
· Integration with automation systems for synchronized operations.
By enabling data collection and remote control, motors contribute significantly to Industry 4.0 objectives.
6. Supporting Customization and Scalability
Electric motors can be configured in countless ways to support unique conveyor requirements—making it easy to scale or modify your operations.
Custom Options Include:
· Different shaft types (solid, hollow, splined)
· Mounting styles (foot, flange, torque arm)
· Brake integration for incline systems
· Explosion-proof designs for hazardous environments
This flexibility allows businesses to tailor conveyor systems for current needs while preparing for future expansion.
![Supporting Customization and Scalability Supporting Customization and Scalability]()
7. Reducing Maintenance and Downtime
Reliable electric motors significantly reduce unplanned maintenance and system downtime, both of which can be costly.
How Motors Help:
· Use of sealed bearings and robust construction for long service life.
· Smart monitoring to detect early signs of wear or failure.
· Compatibility with predictive maintenance tools.
Investing in quality motors translates into higher uptime and productivity.
8. Environmental and Sustainability Impact
Eco-conscious businesses are now focusing on energy-saving motors to meet green goals and reduce their carbon footprint.
Sustainable Advantages:
· Lower CO₂ emissions due to reduced power usage.
· Longer motor life reduces waste from frequent replacements.
· Smart motor control minimizes idle energy consumption.
![Environmental and Sustainability Impact Environmental and Sustainability Impact]()
Types of Electric Motors Used in Conveyor Systems
Not every motor is a one-size-fits-all deal. Conveyor systems use different types depending on the job.
1. AC Induction Motors (Three-Phase)
Overview:
The three-phase AC induction motor is the most commonly used motor in conveyor systems due to its simplicity, durability, and low maintenance needs.
Key Features:
· Robust and long-lasting
· Cost-effective
· Simple to operate with few moving parts
· Available in multiple efficiency ratings (IE2, IE3, IE4)
· Available in multiple type such as Variable Frequency Drive (VFD) Motors, Brake Motors Explosion-Proof Motors
Best For:
![Introduction Introduction]()
2. DC Motors
Overview:
DC motors offer precise speed control, making them ideal for applications that require variable speed or frequent starts and stops.
Key Features:
Best For:
![DC MOTOR in Conveyor System DC MOTOR in Conveyor System]()
3. Gear Motors
Overview:
Gear motors combine an electric motor with a gearbox, which reduces speed and increases torque.
Key Features:
· High torque at low speeds
· Compact and space-saving
· Efficient power transmission
Best For:
![GEAR MOTOR IN CONVEYORS GEAR MOTOR IN CONVEYORS]()
4. Servo Motors
Overview:
Servo motors offer precise control of position, speed, and torque, making them ideal for automation and robotics in conveyor systems.
Key Features:
· High precision and responsiveness
· Works well with feedback systems (encoders)
· Quiet and efficient operation
Best For:
· Conveyor systems in automated production lines
· Pick-and-place conveyor units
· High-speed sorting systems
![SERVO MOTOR in Conveyor System SERVO MOTOR in Conveyor System]()
5. Stepper Motors
Overview:
Stepper motors rotate in fixed increments, offering excellent control over movement and positioning.
Key Features:
· Accurate, repeatable motion
· Open-loop control (no feedback required)
· Easy integration with digital controllers
Best For:
Choosing the Right Electric Motor for Your Conveyor
Picking the perfect motor isn’t rocket science, but it does require some thought. Here’s how to nail it.
1. Understand Your Conveyor Type
Each type of conveyor demands a different motor setup. Understanding how your conveyor works is the first step.
Common Conveyor Types:
· Belt Conveyors – Require motors with smooth, continuous motion.
· Roller Conveyors – Often powered by gear or drum motors.
· Chain Conveyors – Need motors with high torque and low speed.
· Screw Conveyors – Require motors that can handle heavy, slow-moving loads.
· Inclined/Vertical Conveyors – Demand brake motors for safety.
✅ Tip:
Match the motor’s design to the conveyor’s structure and function to ensure compatibility and efficiency.
2. Define Load Characteristics
One of the most crucial steps is calculating the load your conveyor needs to move.
Consider:
· Weight of items
· Conveyor length and width
· Incline or decline angle
· Friction between materials and surface
✅ Tip:
A motor that’s too small will overheat and fail. A motor that’s too large wastes energy. Use a load calculator or consult with engineers for precise sizing.
![Define Load Characteristics Define Load Characteristics]()
3. Matching Motor Power to Load
Size matters when it comes to motors. A motor that’s too small will struggle and burn out, while an oversized one wastes energy. Calculate the load—weight, speed, and duty cycle—and choose a motor with the right horsepower. It’s like picking the right tool for the job; a hammer’s great, but you wouldn’t use it to screw in a lightbulb.
I. Motor Efficiency Standards:
✅ Tip:
Use IE3 or IE4 rated motors to reduce power consumption and qualify for energy rebates in some regions.
II. Duty Types:
✅ Tip:
For 24/7 operations, always select an S1 rated motor to avoid overheating and burnout.
III. Key Factors:
· Voltage (220V, 380V, 415V, 690V)
· Phase (single-phase or three-phase)
· Frequency (50Hz or 60Hz)
✅ Tip:
Most industrial conveyors use three-phase motors due to better efficiency and torque.
IV. Key Formulas:
✅ Tip:
Use gear motors when you need high torque at low speeds—especially for heavy or inclined loads.
![Matching Motor Power to Load Matching Motor Power to Load]()
4. Considering Environmental Conditions
Where’s your conveyor operating? A motor in a clean warehouse faces different challenges than one in a dusty mine. Check the environment for heat, humidity, or debris, and pick a motor built to handle it. Look for models with sealed enclosures or cooling fans to combat tough conditions.
Environmental Factors:
· Moisture or humidity
· Dust and debris
· Temperature extremes
· Corrosive chemicals
Protection Ratings:
· IP55/IP65 – For dust and water resistance
· Explosion-proof – For gas, dust, or chemical-prone environments
5. Select a Proper Gear Ratio (If Needed)
If your application requires torque multiplication or speed reduction, a gearbox is essential.
Gearbox Types:
· Helical – Smooth and quiet
· Worm – Compact with high torque
· Bevel – For right-angle drive systems
✅ Tip:
Choose gear motors when dealing with heavy loads or incline conveyors to maximize torque output.
![Select a Proper Gear Ratio (If Needed) Select a Proper Gear Ratio (If Needed)]()
6. Don’t Forget Maintenance and Serviceability
Choose motors that are easy to maintain and come with strong manufacturer support.
Features to Look For:
✅ Tip:
Document motor specs and schedule preventive maintenance to extend service life.
Summary Table: Key Selection Factors
| Criteria | What to Consider |
| Conveyor Type | Belt, roller, chain, screw, vertical |
| Load Characteristics | Weight, size, friction, incline |
| Motor Type | AC, DC, Servo, Gear, Brake, VFD, Explosion-proof |
| Torque and Speed | Match to load demand and conveyor pace |
| Power Supply | Voltage, frequency, and phase |
| Duty Cycle | Continuous or intermittent operation |
| Environmental Protection | IP rating, explosion-proof, temperature rating |
| Energy Efficiency | IE2, IE3, IE4 ratings |
| Maintenance | Ease of service and spare part availability |
| Automation Compatibility | PLC, VFD, sensors |
Future Trends in Electric Motors for Conveyor Systems
As industries move toward automation, energy efficiency, and digital transformation, the role of electric motors in conveyor systems is evolving rapidly. What was once just a mechanical component is now becoming a smart, connected, and optimized part of the production ecosystem.
Let’s take a deep dive into the future trends shaping electric motors for conveyor systems, and how these innovations will redefine performance, maintenance, and sustainability in industrial operations.
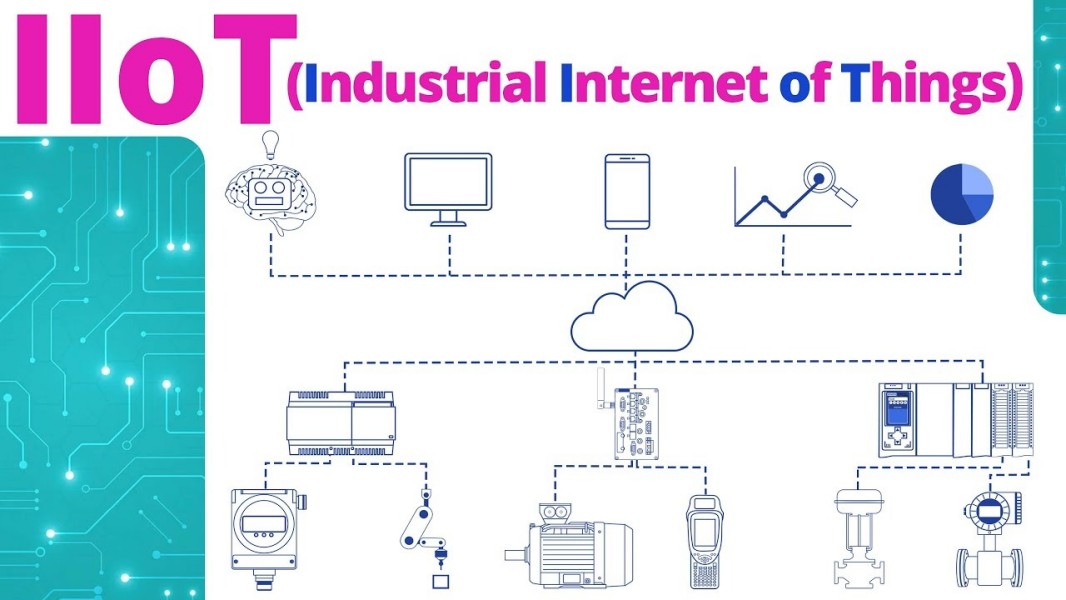
1. Smart and Connected Motors (IIoT Integration)
One of the most prominent trends is the integration of electric motors into the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT).
Key Features:
· Embedded sensors for real-time monitoring of temperature, vibration, and current
· Wireless connectivity (Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, or Ethernet/IP)
· Cloud-based dashboards and analytics
Benefits:
· Enables predictive maintenance and avoids unexpected downtimes
· Provides data-driven insights for performance optimization
· Seamless integration with smart factory ecosystems
![IIoT Integration IIoT Integration]()
2. Increased Use of Energy-Efficient Motors (IE4/IE5)
As global energy regulations tighten, manufacturers are moving toward ultra-high-efficiency motors.
What’s New:
· Adoption of IE4 and IE5 motors with efficiency ratings above 90%
· Use of advanced materials like rare-earth magnets for higher performance
· Reduced CO₂ emissions and operating costs
Benefits:
· Lower energy bills for 24/7 conveyor operations
· Better return on investment (ROI)
· Compliance with environmental standards like Ecodesign and NEMA Premium
3. Integration of Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs) and Intelligent Controls
VFDs are no longer just add-ons—they’re becoming integral to motor design.
Innovations:
· Compact, built-in VFD modules in motors
· AI-based algorithms that automatically adjust speed and torque
· Integration with programmable logic controllers (PLCs) and human-machine interfaces (HMIs)
Benefits:
· Precise speed control across variable loads
· Soft starts and stops reduce mechanical wear
· Adapts dynamically to production demands
Conclusion
Electric motors are the unsung heroes of conveyor systems, powering the belts and rollers that keep industries moving. They bring efficiency, versatility, and cost savings to the table, but they’re not without challenges like overloading or environmental wear. By choosing the right motor, maintaining it well, and keeping an eye on future trends like smart technology, you can ensure your conveyor system runs like a well-oiled machine. So, next time you see a conveyor in action, give a nod to the electric motor making it all happen. Got a motor request? Let me know in the right column—I’d love to connect you!
![Conclusion Conclusion]()
FAQs
1. What type of electric motor is best for conveyors?
Three-phase AC motors or gear motors are commonly used for industrial conveyors, depending on the load and speed requirements.
2. Can I control the speed of a conveyor motor?
Yes! Variable frequency drives (VFDs) allow you to adjust the motor speed precisely.
3. Are electric motors energy efficient?
Modern motors, especially IE3 and IE4 rated, offer high efficiency and can reduce energy costs significantly.
4. How often should I maintain conveyor motors?
Routine checks every 3 to 6 months are ideal, depending on usage.
5. What happens if a motor fails in a conveyor system?
Motor failure can cause the entire system to stop, leading to production delays and costly downtimes.
English
العربية
Français
Русский
Español
Português
Deutsch
italiano
日本語
한국어
Nederlands
Tiếng Việt
ไทย
Polski
Türkçe
Bahasa Melayu
Filipino
Bahasa Indonesia
magyar
Română
Čeština
Монгол
қазақ
Српски
हिन्दी
فارسی
Slovenčina
Slovenščina
Norsk
Svenska
українська
Ελληνικά
Suomi
Հայերեն
Latine
Dansk
Hrvatski
Gaeilge
Eesti keel
Oʻzbekcha
latviešu
Беларуская мова
Български
ქართული
guarani
ʻŌlelo Hawaiʻi
Lietuvių
Lëtzebuergesch
Македонски
Malti
मराठी