How to Connect a Three-Phase Asynchronous Motor: A Comprehensive Guide
Three-phase asynchronous motors power countless industrial applications, delivering robust performance through a unique operating mechanism. Properly connecting these motors ensures optimal efficiency, safety, and longevity. This guide dives deep into the principles, wiring methods, performance differences, and best practices for connecting three-phase asynchronous motors, helping you achieve seamless operation and outrank outdated resources with clear, actionable insights.
![Three-Phase Asynchronous Motor Three-Phase Asynchronous Motor]()
Understanding the Working Principle of Three-Phase Asynchronous Motors
Three-phase asynchronous motors operate using a rotating magnetic field to drive mechanical motion. When you connect the motor’s three-phase stator winding to a three-phase AC power supply, alternating currents flow through the windings. This creates a magnetic field that rotates in space, cutting through the rotor winding to induce an electromotive force and current.
The rotor, influenced by the stator’s magnetic field, experiences electromagnetic forces that cause it to spin. However, the rotor’s speed lags slightly behind the magnetic field’s speed, creating a “slip” that enables continuous energy conversion and power output. Correct wiring is critical to maintaining this process, ensuring the motor runs smoothly and efficiently.
![rotor winding rotor winding]()
Key Wiring Methods: Star vs. Delta Connections
Two primary wiring configurations dominate three-phase asynchronous motor setups: star (Y) connection and delta (△) connection. Choosing the right method depends on the motor’s rated voltage, the power supply voltage, and the operational requirements. Below, we explore these methods in detail.
Star Connection: Structure and Applications
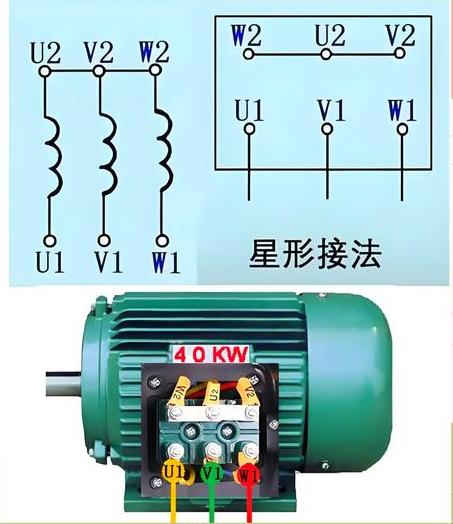
In a star connection, you connect the ends of the three-phase windings to form a neutral point, while the opposite ends link to the three-phase power supply. This configuration suits motors with a rated voltage of 220V operating on a 380V power supply, as it reduces the voltage across each phase winding to approximately 220V.
Star connections are ideal for motors with power ratings of 3kW (4hp) or below, including 0.16hp, 0.24hp, 0.34hp, 0.5hp, 0.75hp, 1hp, 1.5hp, 2hp, and 3hp. The lower voltage across each winding minimizes stress on the motor, making it suitable for light-load or no-load starting scenarios, such as fans or small pumps.
![star connection star connection]()
Delta Connection: Structure and Applications
In a delta connection, you link the three-phase windings head-to-tail, forming a closed loop, with each connection point tied to the three-phase power supply. This method is used when the motor’s rated voltage matches the power supply voltage, typically 380V. Delta connections are common for motors above 3kW, including 5hp, 7.5hp, 10hp, 15hp, 20hp, 25hp, 30hp, 40hp, 50hp, 60hp, 75hp, 100hp, 125hp, 150hp, 180hp, 200hp, 270hp, 340hp, and 430hp.
The delta configuration delivers higher power output and is suited for heavy-load applications, such as cranes or large industrial machinery, where greater starting torque is required.
![triangle connection method triangle connection method]()
Comparing Star and Delta Connections: Key Differences
Understanding the differences between star and delta connections empowers you to select the optimal wiring method for your motor. Below, we break down the distinctions across several critical factors.
1. Winding Configuration
· Star Connection: Connects the ends of the three-phase windings to a central neutral point, with the other ends linked to the power supply. This creates a stable, lower-voltage setup.
· Delta Connection: Forms a closed loop by connecting the windings head-to-tail, with each junction tied to the power supply. This configuration supports higher voltage and power delivery.
2. Voltage and Current Dynamics
When operating on a 380V power supply:
· Star Connection: Each phase winding experiences 220V (380V ÷ √3), and the line current equals the phase current. For example, a motor with a rated current of 10A maintains that current in star configuration.
· Delta Connection: Each phase winding receives the full 380V, and the line current is approximately 1.732 times the phase current (√3). For the same 10A motor, the line current in delta configuration rises to about 17.3A.
This voltage and current disparity directly impacts motor performance and energy consumption.
![electric electric]()
3. Starting Performance
· Star Connection: Produces a lower starting current and torque, making it ideal for light-load or no-load starts. For instance, a fan starting with minimal resistance benefits from star connection to reduce inrush current.
· Delta Connection: Generates a higher starting current and torque, perfect for heavy-load applications like cranes or conveyors that require significant initial force.
4. Power Output and Efficiency
· Star Connection: Delivers lower power output and efficiency but reduces energy consumption, making it suitable for applications with modest power demands, such as small machinery or lightly loaded systems.
· Delta Connection: Offers higher power output and efficiency, ideal for demanding tasks requiring sustained performance. However, it consumes more energy due to the higher current.
![wire winding wire winding]()
5. Application Scenarios
· Star Connection: Best for motors with a 220V rated voltage on a 380V supply or for equipment with light, continuous loads. Examples include ventilation systems or small industrial pumps.
· Delta Connection: Suits motors with a 380V rated voltage on a 380V supply or heavy-load, high-torque applications like industrial presses or large compressors.
Selecting the right connection method hinges on aligning the motor’s specifications with the operational demands and power supply characteristics.
![Applicable scenarios Applicable scenarios]()
Step-by-Step Guide to Wiring a Three-Phase Asynchronous Motor
Proper wiring ensures your motor operates safely and efficiently. Follow these steps to connect a three-phase asynchronous motor correctly:
1. Verify Motor Specifications
Check the motor’s nameplate for its rated voltage, power rating, and recommended connection method (star or delta). Ensure compatibility with the power supply voltage.
2. Select the Wiring Method
Choose star for motors rated at 220V on a 380V supply or for light-load applications (≤3kW). Opt for delta for motors rated at 380V or for heavy-load scenarios (>3kW).
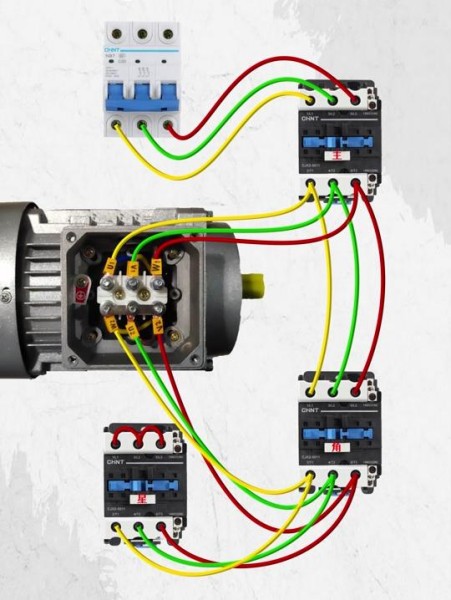
3. Prepare the Wiring
Gather insulated wiring, terminal connectors, and tools like screwdrivers, pliers, and an electrical tester. Ensure all materials meet industrial standards.
4. Connect the Windings
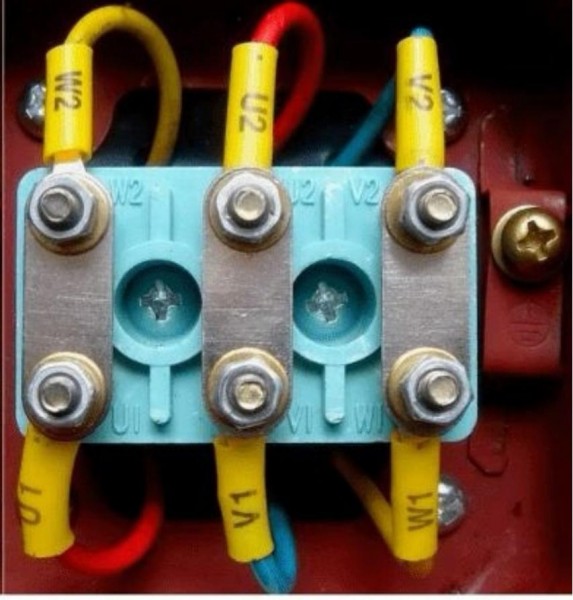
· Star Connection: Link the ends of the three-phase windings (typically labeled U2, V2, W2) to form a neutral point. Connect the starting ends (U1, V1, W1) to the three-phase power supply lines (L1, L2, L3).
· Delta Connection: Connect U1 to V2, V1 to W2, and W1 to U2 to form a closed loop. Attach the connection points to L1, L2, and L3.
5. Secure Connections
Tighten all terminal connections to prevent loosening due to vibration. Use cable ties to organize wiring and reduce strain.
6. Test the Circuit
Use a multimeter to verify continuity and ensure no short circuits exist. Confirm the power supply is off before proceeding.
7. Seal the Terminal Box
Close and seal the motor’s terminal box to protect against dust, moisture, and environmental damage.
![rotor conductor rotor conductor]()
Safety Precautions for Wiring Three-Phase Motors
Safety is paramount when wiring three-phase asynchronous motors. Adhere to these guidelines to prevent accidents and ensure reliable operation:
1. Follow Strict Safety Protocols
· Power Off: Disconnect the power supply before starting any wiring work. Use an electrical tester to confirm the circuit is de-energized.
· Protective Gear: Wear insulating gloves, shoes, and safety goggles to guard against electric shock and arc flash hazards.
· Seal the Terminal Box: After wiring, ensure the terminal box is tightly sealed to prevent dust or moisture ingress, which can degrade insulation.
2. Address Special Situations
· Idle Motors: If the motor has been idle for an extended period, measure the winding’s insulation resistance using an insulation resistance meter. The resistance should be at least 0.5MΩ for low-voltage motors. Dry or re-insulate the motor if the value is lower.
· Phase Loss: If a phase is missing, do not attempt to start the motor. Inspect the wiring, fuses, and contactor contacts to identify and resolve the issue before proceeding.
3. Maintain Regular Inspections
· Check Terminals: Periodically inspect motor terminals for looseness, corrosion, or oxidation. Tighten and clean as needed.
· Monitor Operation: Watch for abnormal temperature, noise, or vibration during motor operation. Stop the motor immediately if issues arise and inspect the wiring and motor condition.
· Frequent Starts: For motors with frequent starts or forward-reverse operations, increase inspection frequency to prevent vibration-induced wiring issues.
![Precautions for wiring Precautions for wiring]()
Optimizing Motor Performance with Proper Wiring
Choosing the correct wiring method enhances motor performance, efficiency, and longevity. Consider these factors when deciding between star and delta connections:
Load Characteristics
· Light loads benefit from star connections due to lower energy consumption. Heavy loads require delta connections for greater torque and power.
Starting Requirements
· Use star connections for reduced starting current in low-torque scenarios. Opt for delta connections when high starting torque is essential.
Energy Efficiency
· Star connections save energy in low-demand applications, while delta connections maximize output in high-demand settings.
By aligning the wiring method with the motor’s specifications and operational needs, you ensure stable, efficient, and cost-effective performance.
Troubleshooting Common Wiring Issues
Even with careful wiring, issues can arise. Here’s how to address common problems:
Motor Fails to Start
· Check for loose connections, blown fuses, or a missing phase. Verify the wiring matches the motor’s rated voltage and connection type.
Excessive Noise or Vibration
· Inspect for loose terminals or unbalanced loads. Ensure the motor is securely mounted and the wiring is intact.
Overheating
· Confirm the motor is not overloaded and the wiring configuration aligns with the load requirements. Check for poor ventilation or insulation issues.
Erratic Performance
· Test the power supply for voltage fluctuations or phase imbalances. Recheck the wiring for errors in star or delta connections.
![Maintenance points Maintenance points]()
Enhancing Motor Longevity with Maintenance
Regular maintenance extends the life of your three-phase asynchronous motor. Implement these practices:
· Routine Inspections: Schedule monthly checks of wiring, terminals, and insulation resistance to catch issues early.
· Cleanliness: Keep the motor and terminal box free of dust, debris, and moisture to maintain insulation integrity.
· Lubrication: Ensure bearings are properly lubricated to reduce friction and prevent overheating.
· Load Monitoring: Avoid overloading the motor, as this can strain the windings and reduce lifespan.
Conclusion: Mastering Three-Phase Motor Connections
Connecting a three-phase asynchronous motor requires a clear understanding of its operating principles, wiring methods, and safety protocols. By choosing between star and delta connections based on voltage, load, and performance needs, you optimize efficiency and reliability. Adhering to safety guidelines and maintaining regular inspections ensures your motor operates at peak performance for years.
Whether you’re powering a small fan or a heavy-duty crane, this guide equips you with the knowledge to wire three-phase asynchronous motors effectively. Apply these insights to enhance your industrial operations and achieve superior results.
English
العربية
Français
Русский
Español
Português
Deutsch
italiano
日本語
한국어
Nederlands
Tiếng Việt
ไทย
Polski
Türkçe
Bahasa Melayu
Filipino
Bahasa Indonesia
magyar
Română
Čeština
Монгол
қазақ
Српски
हिन्दी
فارسی
Slovenčina
Slovenščina
Norsk
Svenska
українська
Ελληνικά
Suomi
Հայերեն
Latine
Dansk
Hrvatski
Gaeilge
Eesti keel
Oʻzbekcha
latviešu
Беларуская мова
Български
ქართული
guarani
ʻŌlelo Hawaiʻi
Lietuvių
Lëtzebuergesch
Македонски
Malti
मराठी